– Prototyping innovation style for a bridge between R&D projects and businesses –
Akira Tezuka (Principal Research Manager) and Katsumi Yonetsu (Invited Senior Researcher) of the Advanced Manufacturing Research Institute (Director: Naoki Ichikawa), the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST; President: Ryoji Chubachi), have published an action toolkit for enhancing effectiveness in design and concept engineering titled “Solution approach and effect measurement method in design and engineering” (Japanese and English versions), in collaboration with Seymourpowell Ltd. of UK.
In contrast to reports of design surveys published by public organizations based on conventional best-practice analyses, this newly published action toolkit describes goals based on current problems recognized from the viewpoint of researchers in collaboration with 14 major manufacturing companies, as well as survey of the present situation, and an R&D process which is one of implementation methods.
In addition to the publication in a website, details of the action toolkit will be presented at SIP Innovative design and production technology symposium 2015 to be held on September 17, 2015 at the National Museum of Emerging Science and Innovation (Miraikan) in Japan, and at International Manufacturing – revisited to be held on September 25, 2015 at the University of Cambridge, UK.
 |
|
Design and concept engineering |
In the manufacturing sector, enhancing design and concept engineering included in front-end activity from the viewpoints of markets and customers to develop high-value products is a new global movement that may make business more efficient. In Japan, in addition to manufacturing of high reliability and quality products, expectations for design and concept engineering that would enhance product and service planning and new market exploring are growing. However, there are serious barriers to the promotion and reform of design and concept engineering.
1) Problems caused by the fact that design and concept engineering are intangible processes unlike manufacturing
-
Poor definition framework: Discussion is difficult due to the ambiguous definition and range of design and concept engineering.
-
Lack of performance measurement methods: Performance measurement against input resources is difficult.
2) Problems caused by the fact that design and concept engineering are practical engineering with confidential information.
-
Lack of collaboration: Companies tend to address problems individually without collaboration with the industry.
-
Poor validation of R&D: Relation between industrial activities and R&D and their validation are insufficient.
As a part of the first year R&D that aims to solve the above mentioned problems, the researchers publish the toolkit to activate a discussion among manufacturing industries towards the solutions of the problems.
This research is carried out as the “Digitization of Design/Engineering Effect” research subject, which is one of the research subjects of the “Design Management for Cross‒disciplinary Teams” project (DMCT; Research Leader: AIST) of a research theme A, “Upstream Delight Design”, in the “Innovative Design and Production Technology Project" (FY2014-FY2018) (Management: NEDO) under the Strategic Innovation Program (SIP) of the Council for Science, Technology and Innovation, the Cabinet Office.
In the Innovative Design and Production Technology Project, researchers are encouraged to conduct “demonstration and implementation of occurring mechanism of innovation, as synergy between revolutionary technology and organizational collaboration, not only by developing a technology but also by trying various innovation styles” and “investigation of a whole scenario covering R&D, practical application and commercialization of R&D results, and deployment in domestic and overseas markets.” Therefore, in DMCT, researchers try an innovation style in which R&D teams, tentative user teams (consortium etc.), and companies planning to commercialize interact each other and carry out R&D incorporating “design thinking” approach. Publication of the toolkit is a part of that trial.
In this research project, relational design is a key term. Design evolved from craft and industrial design to human-centric design in which the relationships between items and humans are designed, and concept engineering evolved from product design to system design, in which the relationships among items are designed. The relational design is an important concept including these two. Managing the relational design properly requires developing a management method and tools for creating the missing links among uncoupled teams, such as users and product development, product development sections and processes, and upstream manufacturing and downstream manufacturing, to make cross-functional team work.
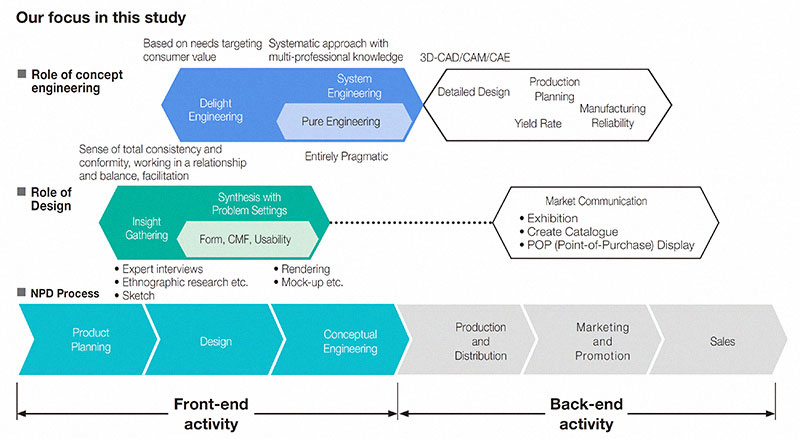
The published toolkit intends to provide a basis for discussion and reform at companies from both a synchronic viewpoint sharing current problems and future goals and a diachronic viewpoint of the five-year R&D project for future design and concept engineering by focusing on the relationship between design and concept engineering, having the process of providing solution and verifying it by R&D, describing both the definition and the domain of design, and proposing a measurement method for design effectiveness. As for an analysis method of current problems and a sharing method of goals, the researchers set up highly challenging tasks, not based on a conventional best-practice analysis, but by capturing the real problems and understanding obstructing factors. This analysis of current problems and goal sharing should foster the development of design. Figure on the first page shows the relationship between design and concept engineering and the domains of them.
The target of this toolkit is new product development (NPD), including service, and the targeted process is the front-end, before the design specifications are set. The researchers focus on the design and concept engineering in the front-end that are collaboratively conducted by many divisions, such as a product planning division, a sales division, and a marketing division.
The researchers selected 14 manufacturing companies (12 cases) considering the balance (or distribution) of the size, field, and characteristics of each company. Based on the interviews with the companies, the researchers compiled the toolkit aiming at the definition and the domain of design and concept engineering, proposing a measurement method for effectiveness, and sharing current problems and goals.
 |
|
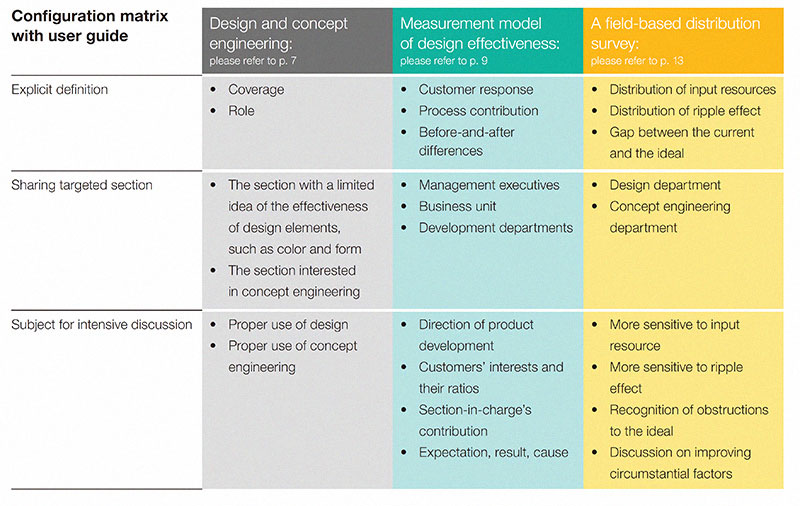
Figure 1: Configuration matrix with user guide of the toolkit |
Figure 1 shows configuration matrix with user guide extracted from the toolkit. It is assumed that showing “sharing targeted section” of “subject for intensive discussion” and “explicit definition” written in the toolkit would induce effective discussion. Two constituent of the toolkit are shown below.
(1) Effectiveness Measurement Formula
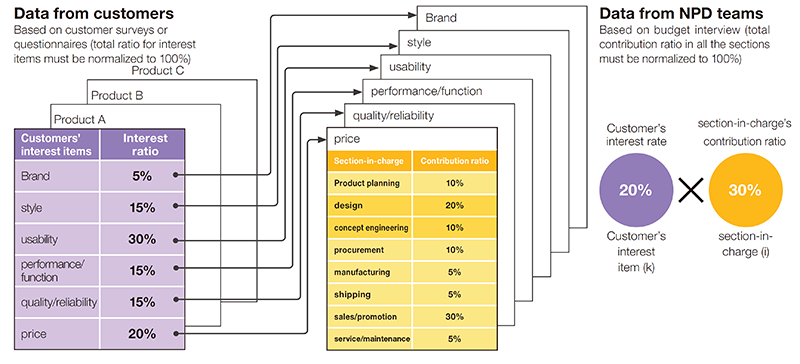
Return on investment (ROI), much discussed in Europa and the US, is one of the effectiveness measurements of design and concept engineering. However, though it might work for outsourcing-based design activities in Europe and the US, it might not be suitable for Japanese manufacturing companies among which in-house design is popular. Though ROI provides numbers for investors, it gives no hints to design and concept engineering sections to improve effectiveness. Thus, the researchers proposed a new type of effectiveness measurement method by introducing the crossing of terms between resource management in product development and customers’ responses, i.e. what customers are interested in and in which part they found value and pay for it, assuming effective uses of results of customer questionnaires accumulated in companies (Fig. 2).
 |
|
Figure 2: Basic idea of the crossing of terms between customers and new product development teams |
(2) Field-based Distribution Survey
The success of design activity depends on the mutual interaction between the uncertainty of the market and customers (i.e., the effectiveness of market research) and the design’s optimal resource allocation (i.e., validation ability). Therefore, a guideline is necessary in order to relate the uncertainty of the market and customers and the design’s optimal resource allocation properly and improve.
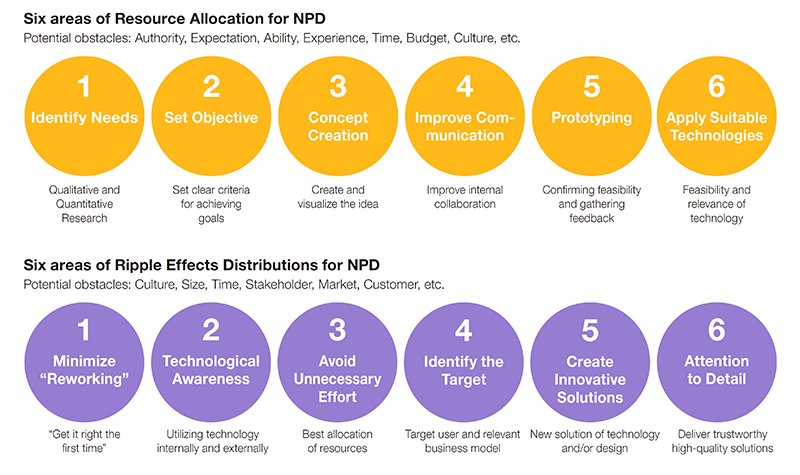
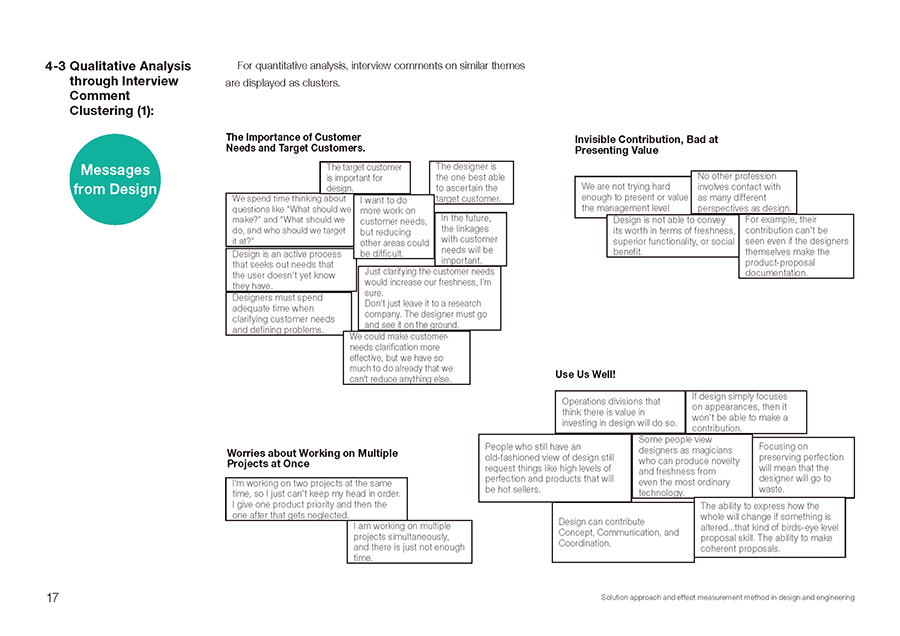
The researchers focused on the present resource allocation and ideal one, the difference in ripple effect distributions, and obstructing factors. They grasped the actual situation at development site through multi-viewpoint interviews with executives, design section, and concept engineering section, understood its tendency by both qualitative and quantitative analyses, and compiled the guideline for the future course of action. Figure 3 shows areas used in the multi-viewpoint interviews to grasp the resource allocation and the ripple effect distributions. Figure 4 visualizes clustering of interview comments by qualitative analysis.
 |
|
Figure 3 Areas used in the multi-viewpoint interviews to grasp the resource allocation and the ripple effect distributions |
 |
|
Figure 4: Clustering of interview comments by qualitative analysis |
The followings are use-cases of the toolkit.
-
Use case #1: Confusion due to the ambiguous definition and range of design and concept engineering
Explanation through figures in this toolkit clarifies misunderstanding and leads to meaningful discussions.
-
Use case #2: Executives’ and business units’ underestimation of the effectiveness of design and concept engineering
This toolkit provides a base for discussion with design and concept engineering sections.
-
Use case #3: The uncertainty about whether your problems are local or common in the industry
This toolkit accurately situates your problems.
-
Use case #4: The uncertainty about the effect of resource distribution for design and concept engineering
The effect measurement method in this toolkit provides a base for discussions about effect measurement.
-
Use case #5: For more efficient collaboration among design, concept engineering, and other sections
Sharing the contents of the toolkit and grasping current efforts and problems push more efficient collaboration.
-
Use case #6: For efficient use of R&D results to reform design and concept engineering activities
Based on the toolkit, R&D to eliminate a gap between a reality and an ideal should be introduced.
-
Use case #7: Evaluation of companies by the innovation style of this project
Sharing problems based on the toolkit leads to more efficient evaluation on companies.
R&D to develop a method and tools for solving the issues described in the toolkit is conducted with the relational design approach is carried out in the project, in order to address the insufficiency in internal marketing (internal collaboration process and team management) and external marketing (external collaboration process and environment). Two more action tools will be published in 2016 and 2018.
 |
|
Figure 5: Action toolset 2014 for experience-value capturing technical design |