The Intelligent Systems Research Institute (ISRI), of the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), an independent administrative institution, has been engaged in a 3-year national project "Consolidation of Software Infrastructure for Robot Development" starting in fiscal year 2002 under "the 21st Century Robot Challenge Program" of the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) and entrusted from the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), another independent administrative organization, in collaboration with the Japan Robot Association (JARA) and Matsushita Electric Works, Ltd.
With the intention of implementing robot systems to meet diversified users' needs, this project has pursued R&D of technologies to make up robots and their functional parts in modular structure at the software level, and to allow system designers or integrators building versatile robots or systems with relative ease by simply combining selected modular parts.
The robot technology middleware having been developed as an infrastructure software for implementing the proposed robot architecture, named "OpenRTM-aist", will be released to the public for the evaluation purpose, so as to accelerate the technological spread and development through feedback from users. Along this line of approach, two prototype systems have been made to ascertain the effectiveness of the developed RT middleware.
-
A robot arm control system based on real time control.
-
A life supporting robot system (RT space), one of promising applications.
 |
 |
|
Photo. 1 An industrial robot (left) and a humanoid arm (right) driven by identical control software as modularized functional parts.
|
The robot industry in Japan has been developed and expanded through the spread of industrial robots for manufacturer's plants in automobile, electric appliance and other industries. Nowadays, Japan is a "big power of robot" producing more than half of industrial robots in the world, and keeping the top-level robot technology internationally.
In the coming society characterized by dwindling birthrate and aging population, shortage of labor power and increase of persons needing nursing care will come to an issue. Under such a circumstance, the development and practical application of robots working in areas other than manufacturing, such as hospitals, welfare facilities and households may be regarded as a promising means of resolution. At present, however, the development of such robots has not yet been made in full scale. While various approaches have been attempted separately for addressing technological problems such as upgrading reliability, safety, operability and amenity for individual robot systems, currently it is extremely difficult to share outcomes of these approaches, the efficiency of robot development has been kept very poor.
As a means for resolving these troubles and advancing the practical application and commercialization of robots for non-manufacturing areas, it has been proposed to develop robot architecture based on modular construction of element robot technologies such as actuators, sensors and control programs and ultimately integrating these modules..
The present study has been carried out under a three-year project "Consolidation of Software Infrastructure for Robot Development" entrusted by NEDO starting from fiscal year 2002. The Project aims at building up a software infrastructure to make robot elements into distributed object modules and to integrate them in a tailor-made way. In this way, an innovative means for robot development to combine robot element modules and an infrastructure technology to enable efficient development based on shared robot technologies will be established. This move is expected to activate robot development in various enterprises, such as medium and small, venture and composite industries, as well as R&D organizations, and to expand the utilization of robots in non-manufacturing areas.
The Project has proposed the construction of custom-made robot system by combining modularized robots and functional components and adding application programs to meet user's requests, and been developing a verifying system to provide services in the living space (RT space), as an example of practical application. (AIST Press Release April 8, 2004).
As a reference implementation software to verify the concept of RT middleware,
OpenRTM-aist has been developed. At first, the open architecture has been examined as shared specifications within the project for ensuring mutual connectivity among modules concerned, and the structure of components has been determined to serve as a framework for defining the standard interface specifications. The RT middleware has been configured as a programming support tool to develope a robotsystem. To be more specific, the system includes a support tool for making RT component, a tool for making combined RT components into a new RT component, and a graphical user interface for linking RT components and making operation control.
While, hitherto, the development and evaluation have been made amongst the project members only, the RT middleware will be released to the public for the purpose of evaluation with the intention of spreading the technology and accelerating the development through technological feedback from users. Domestic users who contacted us will be provided with opportunities for downloading a software package and developer's manual (in Japanese) for OpenRTM-aist from the Project homepage and assessing the program, under the condition of feeding back the result of prototype system development using the RT middleware..
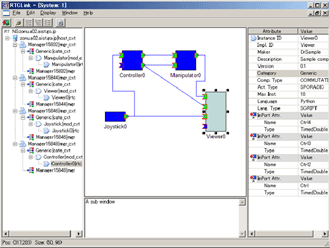 |
Photo. 2 An example of programming support tool in the newly developed RT middleware |
In order to verify the function of the RT middleware, two prototype systems have been constructed: a robot arm control system and a life-supporting robot system, and the effectiveness of the newly developed RT middleware has been corroborated.
As a typical example of robot systems requiring real time control to respond to sensor signals instantaneously, an arm control system has been constructed to be manipulated by a joystick, and it has been confirmed that the use of a development supporting tool provided in the RT middleware facilitates the system construction. To illustrate the effectiveness of the RT middleware, it has been demonstrated that the control system for industrial robot can be made to control a humanoid arm by simply replacing one of components.
 |
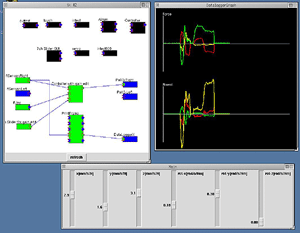 |
Photo. 3 An arm control system manipulated with a joystick, and a program developed by using the RT middleware |
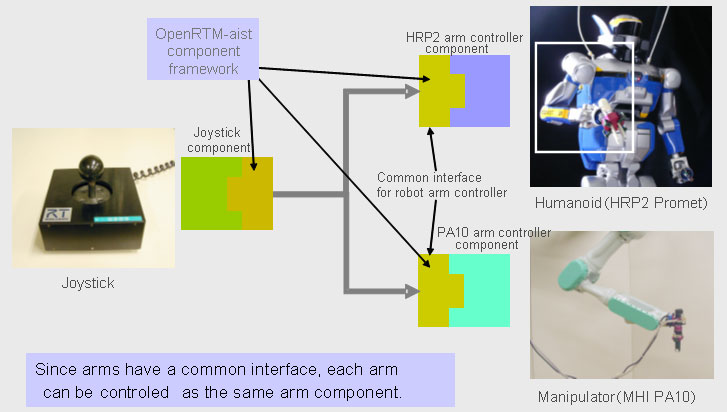 |
Fig. 1 By use of modules sharing a common interface, the control of industrial robot is readily interchangeable with that of humanoid arm. |
As an example of promising applications, a robot system (RT space) has been constructed to support the living through the coordinated actions of robot elements such as sensors and actuators distributed in the living space. In this attempt, various robot element modules have been developed as circumstances demand, and at the same time, the development of RT middleware for the application implementing function involving services and tools for tailoring a robot system in line with users' needs by flexibly combining robot elements has been advanced. It has been confirmed that application programs can be readily developed for ensuring coordinated operation of robot elements within the living space by using the constructed RT space. More specifically, the application programs covering the following functions have been readily built up and modified by using the RT middleware to demonstrate the effectiveness of the latter:
-
Development of life-supporting application programs through the utilization of application program development supporting tool (activity builder).
-
Room monitoring and remote control with mobile phone system.
-
Coordination of RT components in the operation of taking drinks out of a refrigerator by use of a mobile robot..
 |
 |
Photo. 4 Coordinated operation among a life-supporting robot system (RT space), a refrigerator and a mobile robot. |
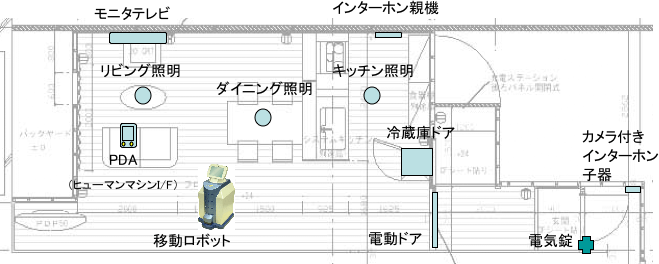 |
Fig. 2 RT components distributed in a living space
|
In the conventional robot system, a slight modification has required an extensive alteration of software. With the newly developed RT middleware, it has been made possible to provide new services by creating a module of new functional part (RT component) for providing necessary functions and posting it in the network, even when user-requested services cannot be implemented with the existing functional parts.