- Preservation of satellites and orbits through a multifunctional robot -
- Aiming to develop the technology for the "Space environment preservation system" of the future -
The Energy Electronics Institute of the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), in cooperation with the University of Tokyo, NEC TOSHIBA Space Systems, Ltd., and Toshiba Corporation, has developed the basic technology for a “Space environment preservation system” using a space robot that operates to maintain the satellite and orbit.
This technology is based on the robotization of space vehicle (space maintenance robot), which allows the assembly of several small satellites in orbit, as well as the capture of orbiting satellites for diagnosis, maintenance and supply. Also, it is used for withdrawal and deorbit of satellites at the end of the mission, helping the preservation of the space environment and contributing to the reliability and increasing life span of space infrastructure composed of small satellites. This multifunctional space robot will provide care “from the cradle to the grave “ for satellite groups.
Currently, there are approximately 9000 pieces of space debris larger than 10cm in diameter orbiting the earth. The amount of this space debris increases at a rate of 300 pieces per year. With a relative velocity of approximately 10 km/s, even small pieces can cause considerable damage to the space vehicles. The amount of fragments produced by chain collision of debris is increasing, raising concerns that it may threaten the future of space activity and indicating that it is time to take measures to protect the space environment.
On the other hand, a system based on a network of a large number of small satellites is required for high quality global personal and mobile telecommunications in our advancing information society as well as for the incessant flow of high-resolution images from Earth observation. To meet these needs, it is necessary to develop a robust information infrastructure which is easy to maintain and to avoid any increase in the amount of debris. As a strategy to solve this problem, we have proposed and carried out the research and development of the “space environment preservation system” which will preserve satellites and orbits. This system is based on a space robot which will provide maintenance to the satellites, and recover, dismantle and dispose of them when they are no longer needed.
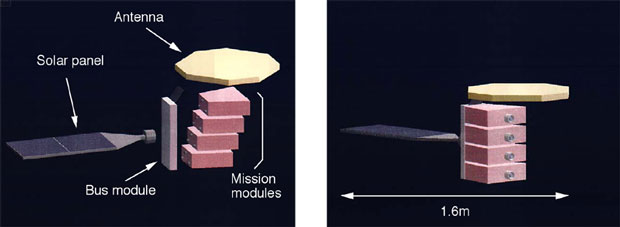
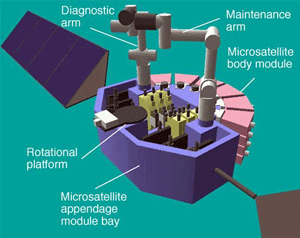
This system calls for the development of a new type of small satellite that can be assembled and maintained by a robot. It also requires the development of the technology that will allow the robot to assemble and capture the satellite, to detect, repair or replace malfunctioning units of the satellite in its orbit, and to collect and carry it out of the orbit at the end of its life span of the satellite.
AIST, pioneer in this field, is engaged in the research and development of this technology. In this opportunity, it has succeeded in applying this technology in a ground demonstration test that includes assembly, capture, module exchange, disassembly and stowing of a small satellite.
This technology is expected to not only be applied to satellites, but also be evolved to a fundamental technology for the transition from disposable space systems to maintainable and recyclable space systems.
 |
 |
 |
|
Assembly of satellite by space maintenance robot |