―Luciferin that changes luminescence color depending on the conformation of IgG―
Researchers) NISHIHARA Ryo, Senior Researcher, KIHARA Yoshiki, Technical Staff (at the time of the research), KURITA Ryoji, attached to the research institute, Health and Medical Research Institute
- Developed an analog of natural luciferin that uses immunoglobulin G (IgG) as a catalyst for luminescence reactions
- Success in changing luminescence color depending on the conformation of IgG
- Potential application in quality assessment of antibodies, since the degree of denaturation can be determined quickly and easily.
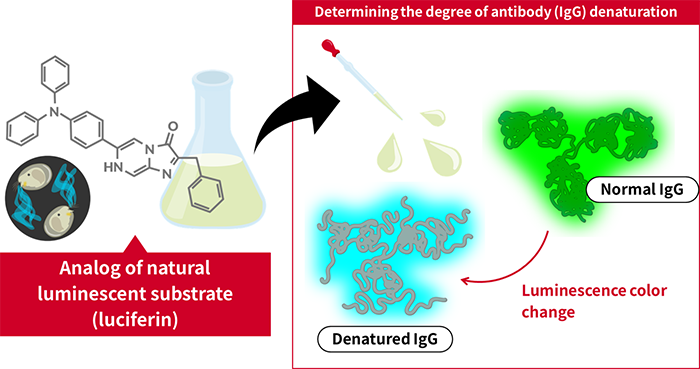
An analog of natural luciferin changes its emission color to reflect the conformational state of antibodies
Antibodies such as immunoglobulin G (IgG) play an important role in recognizing and eliminating viruses and bacteria in vivo and are widely used as diagnostic and therapeutic agents. However, the structure of antibodies is easily affected by storage conditions and the environment, and progressive denaturation impairs their original function. Because antibody denaturation affects product safety and efficacy, the progress of denaturation must be monitored. Currently, analytical methods such as size exclusion chromatography (SEC) and dynamic light scattering (DLS) are used to evaluate antibody denaturation. However, these analytical methods require specialized knowledge and skills. Therefore, there has been a need to develop a method that can evaluate the degree of antibody denaturation more easily and quickly.
Researchers at AIST and Keio University have developed a luminescent substrate (luciferin) that reacts with IgG, an antibody widely used for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes, and changes its emission color according to the structure of IgG.
Antibodies play a role in recognizing and eliminating viruses and bacteria in vivo and are widely used as diagnostic and therapeutic agents. However, antibodies are easily affected by the environment during the manufacturing, storage, and use processes, and their original functions are lost when they are denatured.
In this study, we discovered for the first time that IgG, a type of antibody, has "pseudo-luciferase activity" that catalyzes the luminescent reaction of luciferin. We also developed a denaturing detection technology for IgG that utilizes this activity. Since the emission wavelength of this newly designed and synthesized luciferin changes according to the structure of IgG, the degree of IgG denaturation can be easily and quantitatively evaluated by measuring it. This method has higher sensitivity than the conventional fluorescence analysis method, and since the measurement can be completed within 3 minutes by simply mixing the newly developed luciferin, it is expected to contribute to quality control of antibody drugs related to IgG and to the development of diagnostic agents.
Journal: Analytical Chemistry
Title of paper: Discovery of Pseudo-Luciferase Activity in Immunoglobulin G (IgG) and its Application to the Detection of IgG Denaturation
Authors: Ryo NISHIHARA, Yoshiki KIHARA, Eiji YAMAMOTO, Hidenori HIRANO, Ryoji KURITA
DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5c00646