―Development of a method to measure S-parameters of power devices in a versatile manner―
Researchers) KISHIKAWA Ryoko, Senior Researcher, Research Institute for Physical Measurement, HORIBE Masahiro, Deputy Director, Research Strategy Headquarters
- Developed a probe to connect various shapes of flat electrodes of surface-mount power devices to the S-parameter coaxial test port measurement equipment
- Eliminates the need for test fixtures and calibration devices, required for each electrode shape in the conventional power device testing process
- Aims to reduce the size and the weight of power electronics system
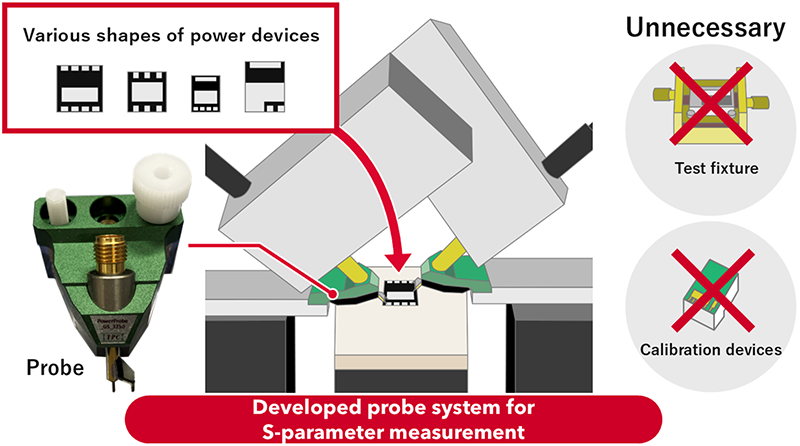
S-parameter measurement of power devices using the developed probe
Power devices are semiconductor devices that efficiently convert electric power (DC or AC) through switching operations to supply the specific load requirement and optimize the power delivery. They are used in a wide range of applications, including mobility (e.g., electric vehicles and trains), renewable energy, and home appliances. In recent years, development of compact and lightweight power electronic systems has been promoted by increasing the switching frequency of power devices.
Traditionally, power electronics that handle high voltages and high currents have been built on a foundation of low-frequency physics, but the development of systems that switch at high frequencies requires the introduction of high-frequency physics as well. This has been one of the technical hurdles in advancing research and development of high-frequency switching. For example, S-parameter measurement, a physical quantity that represents high-frequency characteristics, is essential for efficient power transfer in high-frequency circuits. However, S-parameter measurement requires the preparation of test fixtures for shape transformation to connect the flat electrode of a surface mount power device to the measurement device. In addition, calibration devices must be fabricated for each geometry of the device under test to eliminate the influence of the test fixture from the measurement results. The fabrication of such test fixtures and calibration devices requires design and simulation based on high-frequency physics, which is labor-intensive and costly.
AIST researchers, in collaboration with Techno Probe Co., Ltd and Keysight Technologies, Inc., have developed a system for universally evaluating the high-frequency characteristics of surface mount power devices with various electrode shapes.
Power devices are semiconductor devices that efficiently convert and control electric power by switching large currents on and off at high speeds. They are used in various fields including electric vehicles, railroads, solar power generation, and home appliances. Operating at high switching frequencies makes it possible to reduce the size of power devices, inductors, capacitors, and other components, and is expected to ultimately lead to smaller and lighter systems. To design circuits that operate at high switching frequencies, information on S-parameters, which represent the reflection and transmission of high-frequency signals, is useful.
AIST, Techno Probe Co., Ltd and Keysight Technologies, Inc. have developed a probe that converts coaxial into planar electrodes for surface mount power devices and a probe station to control the probe. The developed probes are compatible with the geometry of multiple types of electrodes and can measure S-parameters from 50 kHz to 1 GHz. This is expected to contribute to the development of compact and lightweight power electronic systems for high switching frequencies operation. This newly developed probe allows for easier and less expensive S-parameter measurement.
The developed probe and probe station will be launched for sale by Techno Probe Co., Ltd for the Japanese market and by T Plus Co. Ltd. for the overseas market.