―Efficiently improve an existing enzyme in a short period of time using computational methods―
Researchers) IKEBE Jinzen, Senior Researcher, KAMEDA Tomoshi, Senior Principal Researcher, Computational Omics Research Team, Artificial Intelligence Research Center
- Molecular dynamics simulations to investigate the properties of enzyme-substrate complex structures
- Simulation results reveal improved enzymes with increased purity and production capacity for l-menthol.
- Enables production of high-purity l-menthol in an economical process with low environmental impact
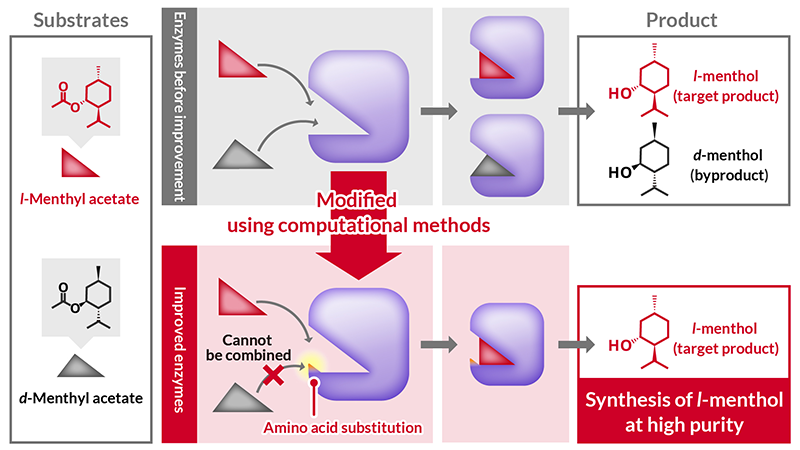
Production of l-menthol by the BCL enzyme
Menthol is a product material with a large economic ripple effect, used in a wide range of applications such as cosmetic fragrances and raw materials for pharmaceuticals, due to its unique minty scent, cooling effect by its cool feeling, and analgesic effect. Its market size is expected to reach $1.193 billion by 2032*. Originally, menthol was produced through the extraction of peppermint and cornmint. However, in recent years, industrial production of menthol has become essential, as increased production from these cultivations can no longer meet demand. Menthol is produced as a mixture of l-menthol, which has industrial value, and d-menthol, a byproduct with significantly inferior taste and odor (see schematic). Reducing the proportion of d-menthol and improving the purity of l-menthol is a critical challenge in industrial synthesis, requiring advanced chemical synthesis processes. Recently, industrial synthesis using biotechnology, which leverages enzymes with substrate specificity has gained attention. In the production of l-menthol, enzymes such as lipases and esterases have proven effective at improving the purity of l-menthol, and research has been conducted on their industrial use. BCL, the subject of this study, is one of the leading candidates.
To use l-menthol directly as a flavoring agent, a purity of 99%ee or higher is required. However, production using conventional BCL has been limited to 98%ee. Since the optical isomers l-menthol and d-menthol have very similar chemical properties, it is difficult to separate them and increase the purity on an industrial scale, and BCL that achieves high purity at the production stage is required.
* https://www.statsmarketresearch.com/menthol-2024-2030-528-7971378
The AIST, in collaboration with Amano Enzyme Inc., has developed enzymes capable of synthesizing high-purity l-menthol, which can be used directly as a flavoring agent, through computational science.
Menthol is widely used as a fragrance in cosmetics and as a raw material in pharmaceuticals because of its distinctive minty scent, cooling effect due to its refreshing coolness, and analgesic effect. In recent years, the demand for menthol has exceeded what can be supplied through extraction from peppermint and cornmint, making industrial production essential. Menthol consists of a mixture of l-menthol, which has high industrial value, and d-menthol, a byproduct with significantly inferior taste and odor. Increasing the purity of l-menthol requires an advanced chemical synthesis process. Biotechnological methods utilizing the substrate specificity of enzymes are therefore attracting attention for the industrial synthesis of higher purity l-menthol.
In this study, new enzymes were developed based on Burkholderia cepacia lipase (BCL), a promising candidate enzyme for the industrial synthesis of l-menthol, using MSPER, an enzyme modification technology developed by AIST based on computational science. Conventional BCL produces l-menthol with a purity (optical purity) of approximately 98%ee, which is less than the 99%ee required for direct use as a flavoring agent. However, the newly developed enzymes achieved an l-menthol purity of up to 99.4%ee. This enzyme development contributes to the production of high-purity l-menthol in an environmentally friendly and economical process.
Details of this technology were published online in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry on February 17, 2025.
Journal: Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
Title of paper: Computational design of Burkholderia cepacia lipase mutants that show enhanced stereoselectivity in the production of L-menthol
Authors: Jinzen Ikebe, Kazunori Yoshida, Satoru Ishihara, Yoichi Kurumida, Tomoshi Kameda
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c09949