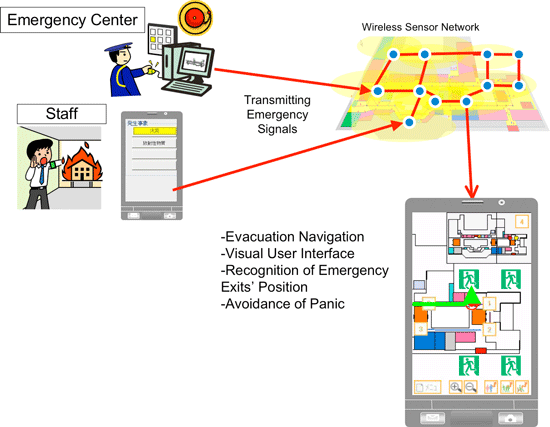
- On receiving emergency signals, automatically provides evacuation navigation -
Koichi Kurumatani (Leader) and others of Multi-Agent Group, Information Technology Research Institute (Director: Satoshi Sekiguchi), the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST; president: Tamotsu Nomakuchi), have developed a robust positioning system utilizing ZigBeeTM (a wireless sensor network on the 2.4 GHz ISM band) that is robust to signal loss, noise, and signal fluctuation due to multipath interference.
Although wireless communication devices operating on the 2.4 GHz ISM band are inexpensive, when these devices are used in a positioning system, they are quite susceptible to signal loss or fluctuation, which prevents reliable and continuous positioning. The developed positioning system applies stochastic reasoning in analyzing the ID and RSSI (received signal strength indication) of received wireless signals. The position of people or target objects can be estimated within a margin of error of from one to several meters regardless of signal loss, noise, or signal fluctuation due to multipath interference.
The developed software implementing stochastic reasoning analyzes IEEE 802.15.4 packets that underlie ZigBeeTM communication protocol. It is significantly less computationally intensive and can even run on mobile phones. Additionally, in order that emergency signals can be transmitted only with the sensor network, all that needed to notify the occurrence of emergencies and their types is prepared in the system. Users' own mobile phones can provide navigation information about shopping or sightseeing under normal circumstances, and once when emergency signals are received, evacuation navigation is automatically invoked, that guides users to the nearest emergency exit. The system has been installed and tested at Landmark Plaza in the Minato Mirai area of Yokohama City and its functionality in a real environment is verified. A variety of applications of this positioning system at public facilities and commercial buildings are expected.
 |
|
Providing evacuation guidance (schematic diagram) |
Practical positioning systems that are robust to signal loss, noise, and multipath interference have been expected to realize means of determining the location and tracking the movement of people and objects indoors. In particular, people have sought the practical adoption of robust positioning systems that can continuously determine location and track movement, using economical, easy-to-install wireless communication systems on the 2.4 GHz ISM band and are accurate to within a few meters regardless of signal loss, noise, or signal fluctuation.
Navigation has been a primary application of positioning systems to date. Thus, systems that provide services related to shopping or event guidance under normal circumstances but switch to evacuation guidance (to emergency exits) in emergencies would give visitors to commercial facilities peace-of-mind as they enjoy a range of other services.
Through the R&D of life safety technology utilizing IT, AIST has sought to develop safety-related services that determine and utilize the current location and physical condition of the public, the elderly, and others. As part of this research, AIST has been developing positioning systems for indoor environments that utilize wireless sensor networks and stochastic reasoning, and AIST holds high potential even on a global level.
Although experiments have been conducted in real environments with indoor positioning systems using low-power wireless systems, wireless sensor networks on the 2.4 GHz ISM band (a more practical approach) are expected to gain popularity. AIST has conducted R&D on systems based on ZigBeeTM, one type of wireless sensor networks on the 2.4 GHz ISM band, and IEEE 802.15.4 protocol. The targets of R&D include robust, low-cost indoor positioning systems and systems with both navigation under normal circumstances and evacuation guidance in emergencies.
This R&D has been conducted with support from "Space Gazer System for Safety and Convenience in Living Environment," a project conducted from FY2005 to 2010 in the contracted Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology (CREST) program of Japan Science and Technology Agency.
This research has produced a practical positioning system based on ZigBeeTM, a particularly low-power type of economical, easy-to-install 2.4 GHz ISM band wireless sensor networks. This positioning system is robust to signal loss, noise, or signal fluctuation, and can transmit emergency signals and provide evacuation navigation in emergencies relying on neither other communication methods nor other equipment.
Conventional positioning systems using wireless signals on the 2.4 GHz ISM band that operate on the principle of TDOA (time difference of arrival) tend to require specialized hardware, which also makes them expensive in general. In contrast, systems that operate on the principle of RSSI are more economical but they present problems; absolute precision is poor because positioning is quite susceptible to signal loss, noise, and signal fluctuation due to multipath interference, and positions of moving objects cannot accurately be determined, namely positioning results change discontinuously and indicated locations are often very different from actual locations. A new stochastic reasoning algorithm has been developed for this system. The software is much less computationally intensive, can even run on mobile phones, and was implemented for a ZigBeeTM , IEEE 802.15.4 wireless sensor network protocol.
In addition to the software, an emergency signal transfer system was developed in the positioning system that can alert users to occurrence of emergencies and their types (fires, accidents, and so on), without affecting positioning precision or the required frequency bandwidth of wireless signals. Building managers need not rely on additional communication methods for transmitting emergency signals. Instead, this system alone is sufficient to notify visitors of emergencies. The convenient navigation information about shopping or sightseeing that users usually view on their mobile phones automatically switches to evacuation guidance when emergency signals are received.
The system has been installed at Landmark Plaza in the Minato Mirai area of Yokohama City and the operation of the system in actual commercial facilities was verified.
Main elements of the present system are as follows:
-
A positioning system, in which signals transmitted in a ZigBeeTM, IEEE 802.15.4 wireless sensor network are analyzed by stochastic reasoning on mobile phones; it determines the location and moving trajectory of people and objects. The stochastic reasoning algorithm is computationally light wright enough to run on mobile phones and it shows robustness to signal loss, noise, and signal fluctuation. The system overcomes the shortcomings of conventional systems such as discontinuous positioning results of target objects.
-
An emergency signal transmission system that uses no additional communication systems; it propagates emergency signals within the positioning system, which notify emergencies and types of the emergencies.
-
An evacuation guidance system, triggered by receiving emergency signals, that continuously conducts positioning while guiding users to nearby emergency exits.
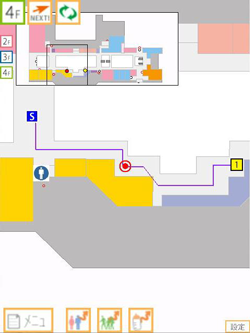
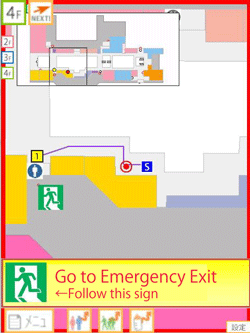
Figure 1 illustrates how, when the navigation system receives emergency signals, it switches from shopping navigation in normal circumstances to evacuation guidance in emergencies.
 |
 |
 |
|
Figure 1 : Examples of evacuation guidance at Landmark Plaza, 4F |
The user's current location is indicated by a red circle in the center of the screen. Here, the first example screenshot shows the navigation screen under normal circumstances, which indicates the route from the origin to the destination via the current location. The second example is the screenshot just after emergency signals are received and the system is switching to provide evacuation guidance to a nearby emergency exit. In the third example is the screenshot after the system has switched to providing evacuation guidance and the screen shows the path to the emergency exit.
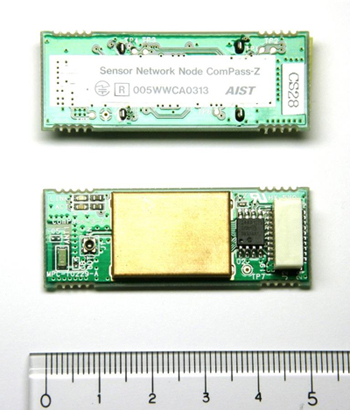
In addition to measuring position, the system can utilize a functionality of transferring sensor data with wireless sensor network such as indoor conditions (temperature, humidity, illumination strength, etc.), and data of cameras and microphones to detect emergency occurrence while providing indoor navigation services to users. Once the ZigBeeTM , IEEE 802.15.4 wireless sensor network is installed, applications to measure environmental conditions, to detect emergencies, and to provide navigation and positioning services, can be incorporated in the same system. Figure 2 shows an IEEE 802.15.4 wireless sensor network device developed for this system. The package includes a chip antenna, and all that is additionally required for operation is power supply. Moreover, because the developed software for the positioning system is generic, it is expected to work on other IEEE 802.15.4-compliant devices.
 |
|
Figure 2 : IEEE 802.15.4 wireless sensor network device developed in this research |
In addition to enabling mobile phone-based positioning and navigation, the software can work as an application of network servers. The potential applications include positioning of users, robot movement support, determining conditions of indoor environments as the primary capability of wireless sensor networks (temperature, humidity, sound, and so on), and detecting emergencies in the monitored area. All of these services can be provided, once one ZigBeeTM wireless sensor network is installed in public facilities or commercial buildings. The system has potential applications including building monitoring/management/services, and robot guidance/management systems.
Notes
ZigBeeTM is a registered trademark of the ZigBee Alliance, a non-profit organization.