Researchers: Atsushi Hozumi, Leader, and Tomoya Sato, Researcher, Advanced Surface and Interface Chemistry Group, Structural Materials Research Institute
The researchers have developed a technique which is able to create a surface initiator layer without any special pretreatment by simply applying a coating solution. They were able to produce polymer brushes on large, commercially useful substrates and it was confirmed that the obtained polymer brush layers are hydrophilic and can be used for electroless plating.
 |
|
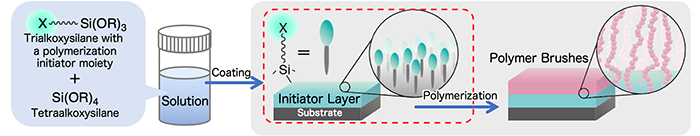
Figure 1. The formation process of a surface initiator layer and a polymer brush layer |
 |
|
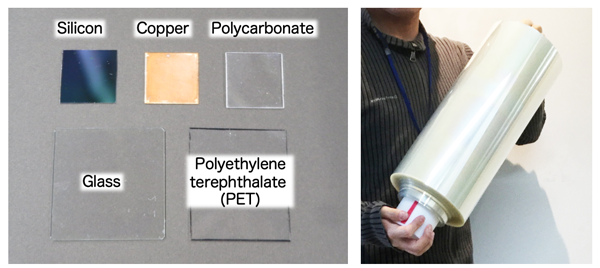
Figure 2. Surface initiator layers formed on various substrates (left) and on a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) film roll (0.4 m × 100 m) (right) |
Polymer brush layers have more durability and stability than conventional polymer coatings and are anticipated to serve as the next-generation coating materials. Unfortunately, precise temperature control, organic solvents, and an air-tight reactor are needed to form the surface initiator layer that serve as a base for the subsequent formation of a polymer brush layer. Given these limitations, the ability to form surface initiator layers on a large scale in air at room temperature is desperately needed.
This newly developed technique uses trialkoxysilanes with attached polymerization initiator moieties and tetraalkoxysilanes to prepare a homogeneous coating solution. Using this method, a large-scale surface initiator layer was easily prepared on a roll of PET film in ambient conditions. In combination with acrylic monomers, the surface initiator layer was used to form polymer brushes on A4-size PET films. The obtained polymer brush layers were hydrophilic and found to be suitable for use in electroless plating.
To further increase the practicality of this technique, the researchers intend to optimize the coating formation and drying steps, specifically by altering the mixing ratios used to form the coating solution and the drying process, respectively. Furthermore, they will seek to increase the amount of substrates and monomers that can be used in this technique.