– Development of a carbon nanotube negative electrode material that suppresses lithium dendrites –
- A negative electrode combining lithium metal and a single-wall carbon nanotube sheet greatly suppresses the growth of lithium dendrites
- Demonstrates five times the current density and cyclic capacity and 20 times or longer life compared to a negative electrode consisting of lithium metal alone
- Single-wall carbon nanotube sheets can be mass-produced, accelerating the practical application of next-generation batteries
Realization of a long-life, large capacity lithium metal electrode using a SGCNT sheet
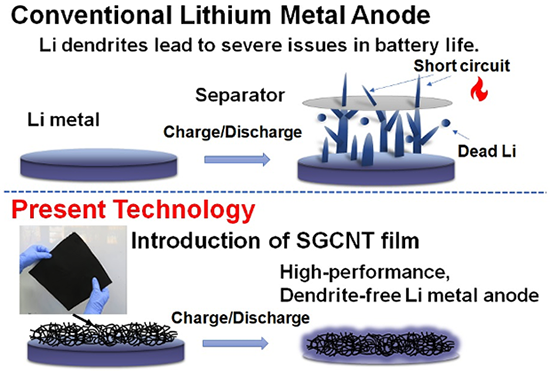
Lithium-ion secondary batteries with lighter weight and larger capacity are demanded with the expansion of applications such as IoT and electric vehicles, and new electrode materials and various types of storage batteries such as all-solid-state batteries, air batteries, and lithium-sulfur batteries are being developed. Among these, lithium metal has a high energy density and is actively studied as a negative electrode material for secondary batteries, but lithium dendrites grow on its surface as the battery is charged and discharged. As a result, there was the issue that the material structure of the battery changes due to factors such as damage to the separator that separates the negative and positive electrodes, leading to a decrease in battery capacity in a short time. For this reason, lithium metal electrodes had not yet been put to practical use. The technology reported here for safe and secure use of lithium metal electrodes is a key technology that dramatically enhances the performance of lithium-ion secondary batteries.
With Zeon Corporation, researchers in AIST developed a technology to suppress dendrites (dendritic crystals) produced during the charging and discharging of lithium metal by the use of a sheet fabricated with super-growth single-wall carbon nanotubes (SGCNT). This technology achieves a high energy density and will contribute to the practical application of large-capacity lithium metal electrodes (negative electrodes)
This technology achieved a vast improvement in lithium metal electrode life by fabricating a SGCNT sheet that has high affinity with lithium, a high specific surface area, and high porosity, and sandwiching it between the separator and the lithium metal electrode. In addition, this SGCNT sheet can be mass-produced, and practical application of high-performance lithium metal electrodes can be expected going forward. Zeon plans to provide samples of the SGCNT sheets.