– Using a tissue culture device to produce living tissues with a primary vessel and capillaries –
Researchers: KIDA Yasuyuki, Leader, MORI Nobuhito, Researcher, AKAGI Yuuka, Researcher, and TAKAYAMA Yuzo, Senior Researcher, Stem Cell Biotechnology Research Group, Cellular and Molecular Biotechnology Research Institute
- Can supply oxygen, nutrients, and drugs by feeding a culture medium into blood vessels
- Can be applied to various tissues (organs and tumors) by changing the cells used as materials and the shape and size of the device
- Contribution to various fields that culture tissues, such as drug discovery and regenerative medicine
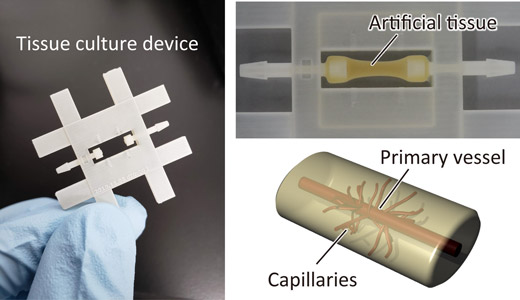
The tissue culture device used and a produced artificial tissue with blood vessels
In fields such as drug development, regenerative medicine, and cancer research, artificial three-dimensional tissues, which mimic human organs and tumors by combining cells and tissue gels, are attracting attention. Expected applications of three-dimensional tissues include pharmaceutical investigation, replacement of lost organs and tissues, and testing of anticancer drugs. However, it was difficult to make in these three-dimensional tissues the large blood vessels (primary vessels) that can deliver liquids like the arteries in actual tissues and the capillaries that branch off from them. It was therefore difficult to efficiently supply oxygen and nutrients to large, thick three-dimensional tissues created to treat lost organs and tissues, or to feed drugs into the inside of three-dimensional tissues for pharmaceutical testing.
The researchers have developed a technology to artificially create tissues with blood vessels with a structure similar to that of actual organs. They produced a large blood vessel (primary vessel) and capillaries that branch off from the primary vessel inside the artificial tissue by mixing collagen (tissue gel) with cells that are the foundation of tissues and blood vessels to cultivate them inside a tissue culture device that can be connected to a liquid feed pump. By feeding a culture medium through the blood vessels, it is possible to supply oxygen and nutrients to maintain large tissues or to feed in a test drug. This technology is expected to contribute to the fields of drug discovery and regenerative medicine.