-Functional Enhancement in Consideration of International Application and Users' Comments -
The Environment Exposure Modeling Team (leader: Dr. Haruyuki Higashino) of the Research Center for Chemical Risk Management (CRM), the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), an independent administrative institution, has developed an English Version and a Revised Edition of the model ADMER for predicting wide area atmospheric concentration distribution and exposed population distribution for chemical substances. The software and user manual will be provided free of charge from January 6, 2005. (These documents can be downloaded from URL http://www.riskcenter.jp/ADMER/.
Outline of ADMER
Full name: AIST -Atmospheric Dispersion Model for Exposure and Risk Assessment (AIST-ADMER). The ADMER is software for assessing spatio-temporal distribution of chemical substance concentrations in a wide district scale, such as Kanto or Kinki Area, allowing to estimate average concentration of chemical substances for a month in six time zones with 5x5 km spatial resolution .
In addition to functions of estimating the distribution of atmospheric concentration and deposits of chemical substances, the ADMER is equipped with features of creating a grid map of emissions, compiling, interpolating and analyzing meteorological data, as well as analyzing estimated concentrations, such as computation of exposed population distribution. Furthermore, basic functions for exposure assessment including graphic user interface to assist computational operation and data management, mapping display for the distribution of emission sources, concentration and deposit and data pickup for particular locality are nearly completely furnished.
Owing to these functions and features, it has become possible to estimate spatio-temporal concentration distribution over an extensive coverage not only for specialists of simulation model, but also for researchers and critics on risk assessment, and persons-in-charge in the national and local governments, as well as in enterprises.
In a year since its first publication of ADMER Ver. 1.0, for the nation-wide coverage, the software has been utilized already by 1,000 or more clients. It is one of the most popular software of this kind in Japan. Currently, the ADMER is being used for various purposes, and diverse places, as listed below.
-
As resources for the implementation of environment policy and for risk communications at the national and local governments,
-
As materials for environment education at educational institutions, NGOs and enterprises, and
-
As background data for responsible care by enterprises.
1. Provision of User Interface and Manual in English
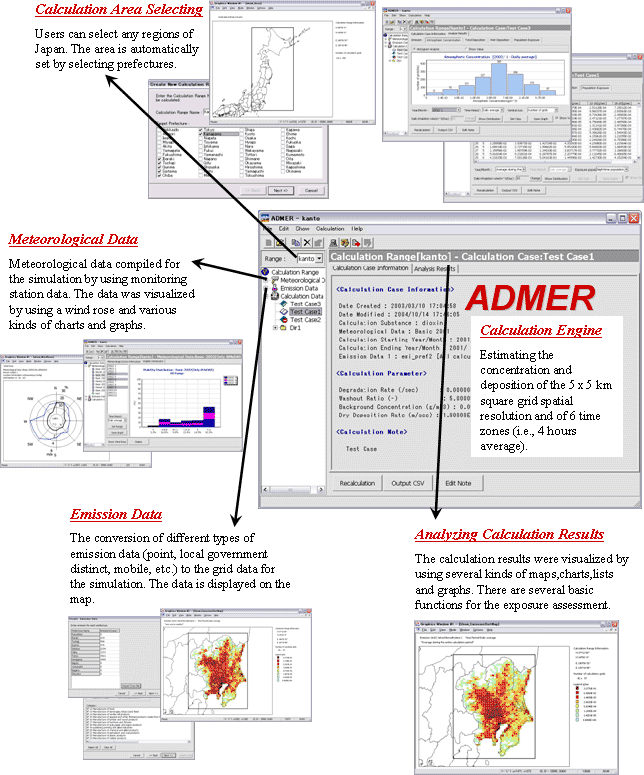
Previously, these documents were available only in Japanese. An English-based user interface Ver. 1.5e has been developed, and made deliverable together with a user manual in English (Fig. 1). While the English edition released is applicable only to the territory of Japan owing to the restriction of built-in data required for model operation, such as population, land utilization and industrial statistics, functional enhancement and data update mentioned below will be available to the English version, too.
The release of English edition will improve the international recognition of the ADMER and augment drastically the access from overseas and foreign users working in Japan. The software is expected to be used for environmental impact assessment prior to entrance to the Japanese market, case studies for Japan in respect to exposure and risk assessment and environment training program for students from developing countries.
 |
|
Fig. 1. User interface and main functions of the English-based ADMER (Ver. 1.5e). |
2. Enhanced Computational, Managerial and Display Functions
(1) Emission Data Management
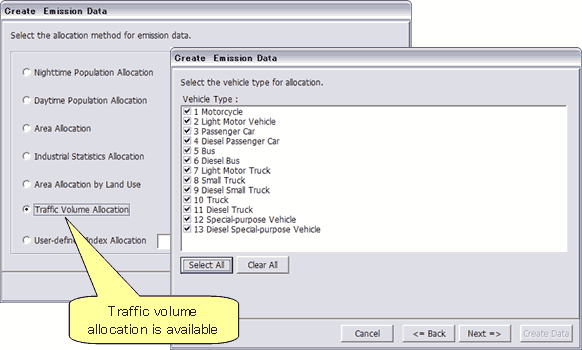
Traffic volume data for different vehicle types as indexes for allotting prefectural and municipal emission data to a grid map (with built-in data for 5x5 km grids for the whole of Japan are made available. (Fig. 2)
Emission data register function is added so that emission data prepared by another PC can be readily used.
 |
|
Fig. 2. Traffic volume for different vehicle types made available as indexes for allotting prefectural emission data to grid map. |
(2) Meteorological Data Management
As the weather data are prepared for smaller sectors so as to alleviate memory restriction, and data preparation for larger coverage area is made available. Meteorological data register function is added so that weather data prepared by another PC is readily used.
(3) Computational Function
The computational model is modified so that the background concentration is reflected in the computation of total deposit and wet deposit. At the same time, the processing program is revised to reduce the memory use and accelerate the speed for dispersion computation.
(4) Analytic Function
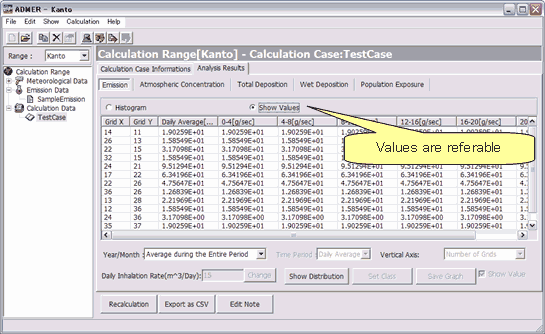
Histogram and tabular display features are added to the analytic function (Fig. 3). This makes it possible to check the computational results rapidly. Output of collective exposure is added to the comma separated value (CSV) format output.
 |
|
Fig. 3. Numeric values for emission and concentration for different grids are made referable. |
With functions enhanced through taking users' comments into consideration, it has been made possible to upgrade the assessment accuracy while keeping simple operation.
In particular, in the Ver. 1.0, it has been necessary to enter emission factors for different vehicle types taken from specialized technical documents to estimate vehicle emissions. Using traffic volume data for allotment makes it possible to estimate regional distribution on the basis of pollutant release and transfer register (PRTR) data (statistics for vehicle sources compiled for different prefectures). This allows assessing the risk of chemical substances attributable to vehicles such as benzene more accurately and by simpler procedures.
3. Built-in Data Updated to Latest Ones and Available Data Types Increased
Built-in meteorological data and social statistic data are updated to the latest ones, as elaborated below
-
Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) data (taken from the JMA Yearbook) covers data up to 2002.
-
Industrial statistics data is updated from the 1998-version to the 2000-version, including business establishment counts in addition to shipments data available previously.
-
For the daytime and night time populations, the link data for 1995-96 are updated to those for 2000-01.
Chronicle of Development
|
March, 2002 |
The First Technical Lecture Course held for test basis with the _ edition under development. |
|
October, 2002 |
The βedition (Ver. 0.8β) with coverage limited to Kanto Area disclosed. |
|
August, 2003 |
The Ver. 1.0 to cover any area of Japan disclosed. |
|
October, 2003 |
The Second Technical Lecture Course held. |
|
January, 2005 |
The English-based edition (Ver. 1.5e) and the revised edition (Ver. 1.5) disclosed simultaneously. |
The development of AIST-ADMER has been carried out as a part of a contract project "Risk Evaluation, Development of Risk Evaluation Method and Analysis of Risk Avoiding Effect of Management Measures" entrusted by the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), another independent administrative organization (President: Dr. Tsutomu Makino).
The future efforts will be focused on the development of a subgrid module, to estimate the concentration distribution in a grid system finer than the basic grid spacing of ADMER (5x5 km), an international edition to expand the coverage of the English Edition to areas beyond Japan, and the application to areas where risk evaluation is essential, such as China.